图中可以看出,函数的导数等于原函数向左平移一个单位。 当k取其它整数时,也可以得到满足条件的其它函数,比如k = 1时,a = 2.98284,b = - 7.72513,此时函数图像如下所示.
- Details Arguments x, y, legend are interpreted in a non-standard way to allow the coordinates to be specified via one or two arguments. If legend is missing and y is not numeric, it is assumed that the.
- Fp = fplot returns a function line object or parameterized line object, depending on the type of plot. Use the object to query and modify properties of a specific line. For details, see FunctionLine.
Produce 2-D plots.
Many different combinations of arguments are possible. The simplestform is
where the argument is taken as the set of y coordinates and thex coordinates are taken to be the range 1:numel (y).
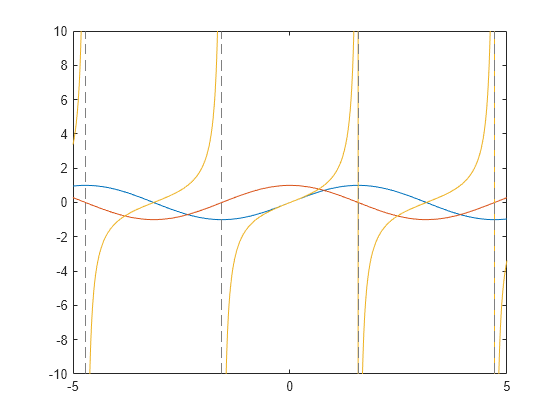
If more than one argument is given, they are interpreted as
or
or
and so on. Any number of argument sets may appear. The x andy values are interpreted as follows:
- If a single data argument is supplied, it is taken as the set of ycoordinates and the x coordinates are taken to be the indices ofthe elements, starting with 1.
- If x and y are scalars, a single point is plotted.
squeeze()is applied to arguments with more than two dimensions,but no more than two singleton dimensions.- If both arguments are vectors, the elements of y are plotted versusthe elements of x.
- If x is a vector and y is a matrix, thenthe columns (or rows) of y are plotted versus x.(using whichever combination matches, with columns tried first.)
- If the x is a matrix and y is a vector,y is plotted versus the columns (or rows) of x.(using whichever combination matches, with columns tried first.)
- If both arguments are matrices, the columns of y are plottedversus the columns of x. In this case, both matrices must havethe same number of rows and columns and no attempt is made to transposethe arguments to make the number of rows match.
Multiple property-value pairs may be specified, but they must appearin pairs. These arguments are applied to the line objects drawn byplot. Useful properties to modify are 'linestyle','linewidth', 'color', 'marker','markersize', 'markeredgecolor', 'markerfacecolor'.See ‘Line Properties'.
The fmt format argument can also be used to control the plot style.It is a string composed of four optional parts:'<;displayname;>'.When a marker is specified, but no linestyle, only the markers areplotted. Similarly, if a linestyle is specified, but no marker, thenonly lines are drawn. If both are specified then lines and markers willbe plotted. If no fmt and no property/value pairs aregiven, then the default plot style is solid lines with no markers and thecolor determined by the 'colororder' property of the current axes.
Format arguments:
| ‘-' | Use solid lines (default). |
| ‘--' | Use dashed lines. |
| ‘:' | Use dotted lines. |
| ‘-.' | Use dash-dotted lines. |
| ‘+' | crosshair |
| ‘o' | circle |
| ‘*' | star |
| ‘.' | point |
| ‘x' | cross |
| ‘s' | square |
| ‘d' | diamond |
| ‘^' | upward-facing triangle |
| ‘v' | downward-facing triangle |
| ‘>' | right-facing triangle |
| ‘<' | left-facing triangle |
| ‘p' | pentagram |
| ‘h' | hexagram |
| ‘k' | blacK |
| ‘r' | Red |
| ‘g' | Green |
| ‘b' | Blue |
| ‘y' | Yellow |
| ‘m' | Magenta |
| ‘c' | Cyan |
| ‘w' | White |
';displayname;'Here 'displayname' is the label to use for the plot legend.
The fmt argument may also be used to assign legend labels.To do so, include the desired label between semicolons after theformatting sequence described above, e.g., '+b;Key Title;'.Note that the last semicolon is required and Octave will generatean error if it is left out.
Here are some plot examples:
Plot Legend Matlab

Plot Legend Of Tarzan Movie
This command will plot y with red circles, y2 with solidlines, y3 with solid magenta lines, and y4 with pointsdisplayed as ‘+'.

If more than one argument is given, they are interpreted as
or
or
and so on. Any number of argument sets may appear. The x andy values are interpreted as follows:
- If a single data argument is supplied, it is taken as the set of ycoordinates and the x coordinates are taken to be the indices ofthe elements, starting with 1.
- If x and y are scalars, a single point is plotted.
squeeze()is applied to arguments with more than two dimensions,but no more than two singleton dimensions.- If both arguments are vectors, the elements of y are plotted versusthe elements of x.
- If x is a vector and y is a matrix, thenthe columns (or rows) of y are plotted versus x.(using whichever combination matches, with columns tried first.)
- If the x is a matrix and y is a vector,y is plotted versus the columns (or rows) of x.(using whichever combination matches, with columns tried first.)
- If both arguments are matrices, the columns of y are plottedversus the columns of x. In this case, both matrices must havethe same number of rows and columns and no attempt is made to transposethe arguments to make the number of rows match.
Multiple property-value pairs may be specified, but they must appearin pairs. These arguments are applied to the line objects drawn byplot. Useful properties to modify are 'linestyle','linewidth', 'color', 'marker','markersize', 'markeredgecolor', 'markerfacecolor'.See ‘Line Properties'.
The fmt format argument can also be used to control the plot style.It is a string composed of four optional parts:'<;displayname;>'.When a marker is specified, but no linestyle, only the markers areplotted. Similarly, if a linestyle is specified, but no marker, thenonly lines are drawn. If both are specified then lines and markers willbe plotted. If no fmt and no property/value pairs aregiven, then the default plot style is solid lines with no markers and thecolor determined by the 'colororder' property of the current axes.
Format arguments:
| ‘-' | Use solid lines (default). |
| ‘--' | Use dashed lines. |
| ‘:' | Use dotted lines. |
| ‘-.' | Use dash-dotted lines. |
| ‘+' | crosshair |
| ‘o' | circle |
| ‘*' | star |
| ‘.' | point |
| ‘x' | cross |
| ‘s' | square |
| ‘d' | diamond |
| ‘^' | upward-facing triangle |
| ‘v' | downward-facing triangle |
| ‘>' | right-facing triangle |
| ‘<' | left-facing triangle |
| ‘p' | pentagram |
| ‘h' | hexagram |
| ‘k' | blacK |
| ‘r' | Red |
| ‘g' | Green |
| ‘b' | Blue |
| ‘y' | Yellow |
| ‘m' | Magenta |
| ‘c' | Cyan |
| ‘w' | White |
';displayname;'Here 'displayname' is the label to use for the plot legend.
The fmt argument may also be used to assign legend labels.To do so, include the desired label between semicolons after theformatting sequence described above, e.g., '+b;Key Title;'.Note that the last semicolon is required and Octave will generatean error if it is left out.
Here are some plot examples:
Plot Legend Matlab
Plot Legend Of Tarzan Movie
This command will plot y with red circles, y2 with solidlines, y3 with solid magenta lines, and y4 with pointsdisplayed as ‘+'.
This command will plot the data in the variable b,with points displayed as ‘*' and a marker size of 10.
Plot Legend Python
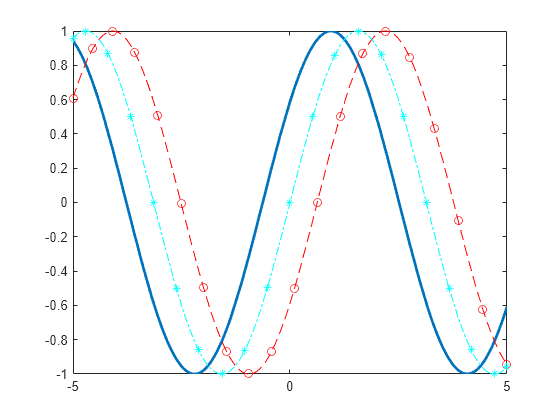
This will plot the cosine and sine functions and label them accordinglyin the legend.
If the first argument hax is an axes handle, then plot into this axis,rather than the current axes returned by gca.
The optional return value h is a vector of graphics handles tothe created line objects.
Plot Legends Of The Fall
To save a plot, in one of several image formats such as PostScriptor PNG, use the print command.
Plot Legend Outside Of Plot R
See also: axis, box, grid, hold, legend, title, xlabel, ylabel, xlim, ylim, ezplot, errorbar, fplot, line, plot3, polar, loglog, semilogx, semilogy, subplot.
